
Hybrid cloud orchestration isn’t just another IT trend—it’s becoming the backbone of modern AI strategy. As enterprises juggle on‑premises systems, public clouds, edge devices and emerging quantum services, the ability to coordinate resources seamlessly determines how fast they can innovate and how well they can control costs. This article demystifies hybrid cloud orchestration, explains why it’s essential, and offers a step‑by‑step playbook for adopting it effectively.
Question: How does hybrid cloud orchestration accelerate AI workflows while reducing risk and cost?
Answer: Hybrid cloud orchestration is the process of coordinating multiple automated tasks across private, public and edge environments so that applications run efficiently, securely and at scale. It goes beyond simple automation by handling dependencies, scaling workloads and enforcing policies across heterogeneous platforms. With cloud costs rising and data‑residency laws becoming stricter, organizations are turning to hybrid strategies that balance performance, compliance and cost. Gartner’s 2025 tech trends elevate hybrid computing—blending edge, cloud and quantum computing—to a top strategic priority.
The digital landscape has outgrown the confines of a single cloud provider. Hybrid cloud orchestration involves coordinating workloads across on‑premises servers, private clouds and public cloud services, so they operate as one cohesive platform. This orchestration ensures resources are provisioned, scaled and decommissioned in the right order, with dependencies respected and policies enforced.
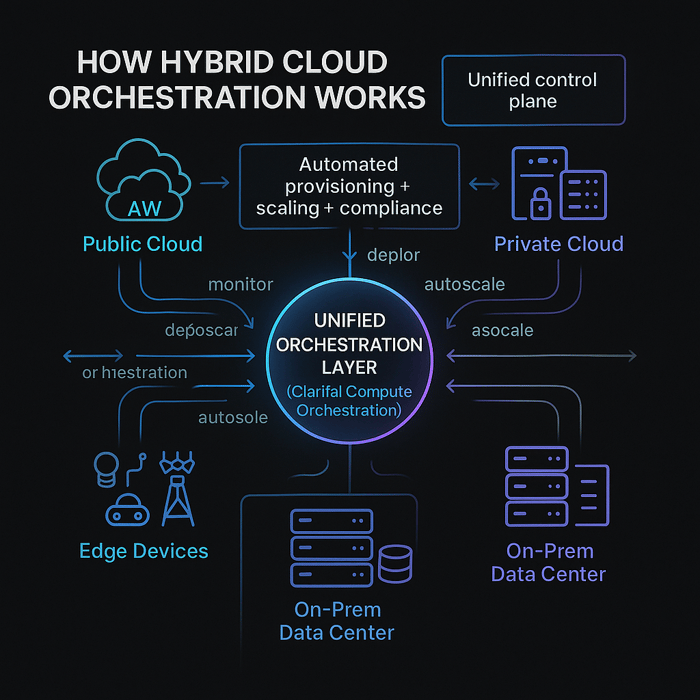
Recent surveys report that nearly half of IT leaders deem hybrid cloud critical for operations. Organizations are even repatriating workloads from public cloud back to private infrastructure due to unexpected costs and security concerns. Thought leaders note that a one‑cloud‑fits‑all approach has lost momentum; hybrid and multi‑cloud reduce risk and improve uptime.
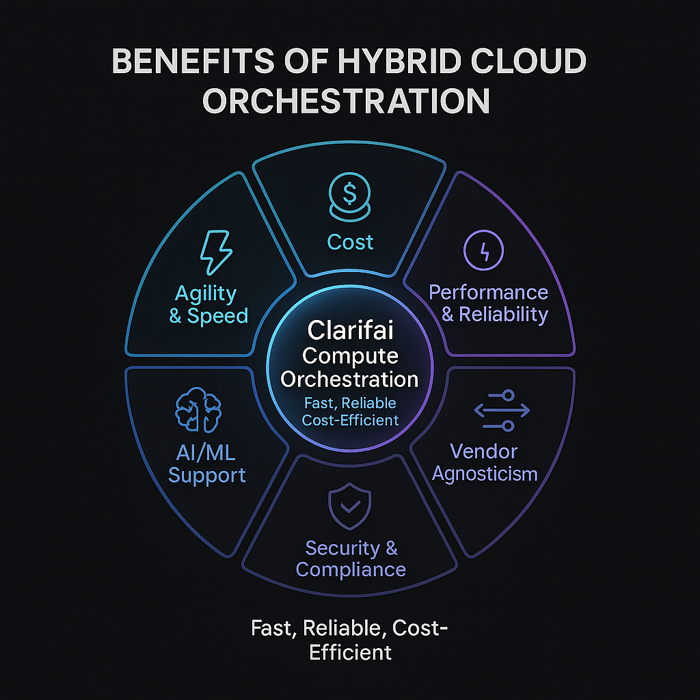
Hybrid orchestration isn’t just a tactical solution—it provides strategic advantages that empower AI workflows and business resilience.
Coordinated workflows replace ad‑hoc scripts, enabling rapid, reliable deployments. Clarifai’s compute orchestration codifies AI deployment routines; customers report up to 3.7× reduction in compute usage while supporting over a million inference requests per second. This agility accelerates experimentation, allowing teams to deploy models across any environment without rewriting code.
Auto‑scaling and resource scheduling allow workloads to scale down automatically when demand drops. GPU fractioning—dividing a GPU into multiple logical partitions—reduces idle capacity and lowers compute costs by more than 70 %. FinOps platforms provide visibility and governance, ensuring budgets are met.
By processing data locally (edge or on‑prem) and tapping cloud resources for heavy lifting, hybrid architectures deliver low latency and high throughput. Replication across environments ensures high availability and disaster recovery.
Orchestration abstracts provider‑specific APIs, enabling workload mobility across clouds. This reduces vendor lock‑in and opens the door to negotiate better pricing.
Sensitive data stays on‑premises while the cloud handles scalable compute. Policy‑driven access, encryption and identity management enforce compliance across jurisdictions.
Clarifai’s unified control plane allows models from any framework to run on shared or dedicated compute, on‑prem or air‑gapped hardware. This flexibility ensures AI models are deployed securely and at scale, with features like autoscaling, containerized packaging, local inference runners and continuous batching.
Choosing the right tools is foundational. Below are key categories and examples to consider (adjusted to avoid naming competitor products directly).
IaC tools let you define infrastructure declaratively. Popular options include open‑source frameworks for multi‑cloud provisioning and cloud‑provider solutions such as AWS CloudFormation. These tools ensure reproducibility and version control and can integrate with orchestration pipelines.
Tools for configuration management automate software installation and system configuration across environments. They allow you to maintain consistency, enforce desired state and reduce configuration drift. Common examples include widely adopted frameworks like Ansible and Puppet.
Kubernetes has emerged as the de facto standard for orchestrating containers. It handles deployment, scaling and management of containerized applications across clusters. Variants like K3s target edge environments, while enterprise distributions provide additional security and operational tooling. Orchestration platforms often integrate with Kubernetes to manage compute across clusters.
Data and AI pipelines require orchestration of dependent tasks. Frameworks such as Apache Airflow, Prefect, Dagster and Argo allow you to define DAGs (directed acyclic graphs) and automate complex workflows. These orchestrators integrate with cloud services, databases and machine‑learning frameworks.
A hybrid control plane unifies operations across clouds and on‑premises. Solutions like open‑source cross‑cloud orchestrators and service brokers provide unified APIs for provisioning resources across providers. Clarifai’s compute orchestration can be considered an AI‑specific control plane: it offers a vendor‑agnostic interface to deploy models on any hardware (GPUs, CPUs, FPGAs) and any environment, with built‑in autoscaling and monitoring.
Serverless computing abstracts the infrastructure completely. Cloud provider services orchestrate functions and manage state for workflows. Open‑source alternatives like Knative and OpenFaaS enable serverless on Kubernetes clusters. Academic research introduces hybrid cloud schedulers that run serverless batch pipelines across public cloud and private edge to save costs and meet deadlines.
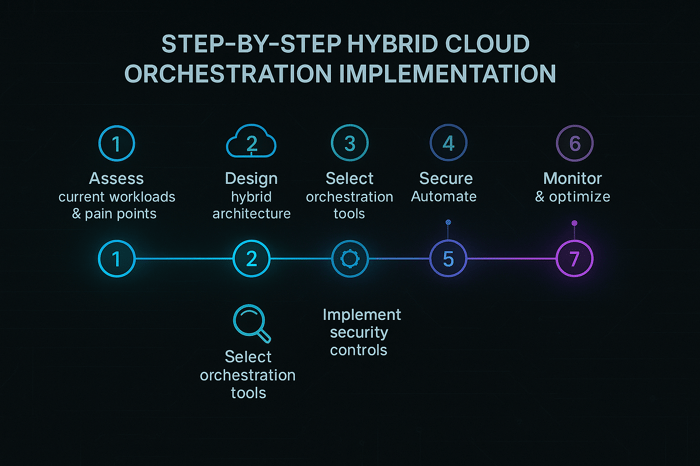
Transitioning to a hybrid model can be complex. This structured approach helps ensure success.
Begin with a comprehensive inventory of workloads, latency requirements and compliance obligations. Identify which workloads need proximity to users, which demand high compute, and where data residency rules apply.
Define where each component should reside. For example, sensitive databases may remain on‑prem while AI inference services run at the edge, and data lake analytics reside in the cloud. Plan network connectivity—VPNs, SD‑WAN, dedicated interconnects—and factor in redundancy and throughput.
Choose IaC, configuration management and orchestrators that support your chosen environments. For AI workloads, evaluate Clarifai’s compute orchestration for unified deployment, or open‑source alternatives like Kubeflow.
Adopt a zero‑trust model: every access is authenticated, authorized and monitored. Encrypt data at rest and in transit; enforce data residency; implement identity and access management across clouds.
Codify deployment pipelines. Use CI/CD to trigger orchestrated workflows that provision resources, deploy applications, and configure services. Integrate autoscaling; GPU fractioning can maximize hardware utilization.
Instrument your hybrid stack with observability tools—logs, metrics and traces. Implement FinOps practices: track costs, set budgets and forecast usage. Integrate sustainability metrics (carbon emissions) into decision‑making.
Iterate by reviewing performance, costs and compliance. Employ AI/ML algorithms to predict demand and perform predictive scaling. Update policies as regulations evolve.
Hybrid architectures aren’t without hurdles. Below are common challenges and strategies to overcome them.
Managing multiple platforms increases complexity. Teams need expertise in both cloud‑native and legacy systems.
Mitigation: Invest in training and certification; leverage managed services; adopt automation to simplify operations. Clarifai’s platform hides infrastructure complexities, allowing developers to focus on models rather than hardware.
Edge and cloud integration can introduce network latency.
Mitigation: Use edge computing to process time‑sensitive data locally. Employ content delivery networks (CDNs), caching and data partitioning. Monitor latency continuously.
Hybrid environments expand the attack surface. Without unified monitoring, misconfigurations can expose data.
Mitigation: Implement zero‑trust security; automate configuration scanning; deploy unified logging and SIEM tools. Adopt encryption by default and enforce least‑privilege access.
Without visibility, hybrid environments can overspend.
Mitigation: Practice FinOps (see next section) and use autoscaling and GPU fractioning to match resource supply with demand.
Different cloud providers have proprietary services.
Mitigation: Use open standards, containerization and vendor‑agnostic orchestration (e.g., Clarifai). Cross‑cloud service brokers allow workloads to move freely.
Regulations on data residency and privacy add complexity.
Mitigation: Classify data by sensitivity; configure geo‑fencing; implement continuous compliance monitoring and audit trails.
Imagine a computer‑vision startup that analyzes medical images. Training large models requires thousands of GPU hours; inference workloads require millisecond latency. Hybrid orchestration allows them to train models in the cloud and deploy low‑latency inference at hospital edge servers. Clarifai’s platform can handle 1.6 million inference requests per second with high reliability, using autoscaling to meet surge demand.
Healthcare providers are using edge devices for patient monitoring. Edge sensors capture vitals and local AI models trigger immediate alerts, while aggregated data is sent to the cloud for analytics. In smart factories, hybrid orchestration coordinates assembly robots and monitors equipment health, reducing production delays.
Recent research proposed a hybrid cloud scheduler (HCS) that runs serverless batch pipelines across public clouds and private edges, reducing costs and meeting deadlines. This shows future potential for hybrid serverless architectures.
Financial services firms are migrating risk‑analysis workloads to hybrid platforms. Data is collected on‑premise for compliance, processed via AI pipelines orchestrated in the cloud (using Airflow or Prefect), then results are synchronized back to local systems. This strategy improves model accuracy and reduces time to insights.
Hybrid orchestration makes multi‑site replication seamless, ensuring that critical data and applications are available even if one region suffers an outage. For example, a media company replicates live video streams across on‑prem servers and two cloud regions, automatically failing over via the orchestrator.
The near future of cloud architecture involves more than just computers. AI, quantum and sustainability are reshaping how we orchestrate workloads.
Machine‑learning algorithms can predict demand patterns, detect anomalies and self‑heal infrastructure. Clarifai uses AI to decide when to scale GPU resources and to pack multiple models efficiently, improving throughput and reducing cost.
Gartner’s 2025 trends highlight agentic AI—autonomous agents that act on behalf of users within hybrid frameworks. These agents leverage the edge for quick decisions and the cloud for deep learning. By 2025, they could help IT teams by autonomously scaling resources, troubleshooting issues and optimizing costs.
Next‑generation FinOps tools incorporate AI to forecast budgets, predict usage and enforce policies automatically. They integrate carbon metrics and sustainability goals into cost analysis, driving responsible computing.
5G and IoT proliferation will create tens of billions of connected devices. Orchestration must handle real‑time workloads across edge and cloud, balancing latency and compute demands.
Quantum computing is becoming accessible through Quantum‑as‑a‑Service (QCaaS) platforms. By 2025, enterprises can test optimization algorithms for logistics or drug discovery via cloud‑based quantum processors. Hybrid orchestrators will integrate quantum tasks into classical workflows.
Security models are shifting towards zero‑trust frameworks that enforce least‑privilege access. AI enhances these models by detecting threats in real time. Confidential computing isolates sensitive data during processing.
Environmental concerns make energy efficiency a priority. Cloud providers offer carbon footprint tools and renewable energy options. Hybrid orchestrators can schedule workloads based on carbon intensity of power grids.
Vertical clouds tailor compliance, data models and workflows for industries like healthcare or finance. The emerging supercloud concept envisions a unified platform that spans all providers, abstracting differences entirely and delivering services seamlessly across them.

Managing costs across hybrid environments requires discipline and modern tools.
FinOps is a collaborative practice that brings together finance, engineering and operations to control cloud spending. It focuses on forecasting, budgeting and optimization and uses actionable metrics to inform decisions. Enterprises that rushed to the cloud often experienced a “cloud hangover” when costs spiralled. FinOps practices help prevent this.
AI algorithms forecast resource usage and recommend instance types. They factor in time‑of‑day, seasonality and business cycles to predict cost spikes, enabling proactive adjustments.
Clarifai’s compute orchestration reduces costs through GPU fractioning and autoscaling, lowering compute expenses by up to 70 %. It integrates with FinOps dashboards so teams can monitor costs across clusters and adjust inference workloads on the fly.
The next few years will reshape how hybrid cloud orchestration operates.
By 2027, hybrid and multi‑cloud will be the default operating model, with AI‑powered systems orchestrating workloads across providers automatically. Organizations will choose the best service for each task, and orchestrators will handle complexity.
Agentic AI will take over routine tasks, enabling self‑driving IT operations. Systems will scale, heal and optimise themselves without human intervention.
As quantum computing matures, hybrid orchestrators will schedule quantum functions for complex optimization problems. Industry‑specific clouds will expand, and the concept of supercloud—a unified overlay across all providers—will gain traction.
Green initiatives will make carbon awareness a requirement. Workloads will be scheduled based on energy source carbon intensity. Organizations will measure success not just in dollars but in carbon saved.
Zero‑trust and confidential computing will become the norm. AI will analyze behavior patterns to detect anomalies and prevent breaches automatically.
Tools that abstract infrastructure complexity—low‑code/no‑code platforms—will empower non‑developers to build applications. Serverless computing will continue to grow, supporting more complex AI and IoT workloads.

Q1: What differentiates hybrid cloud orchestration from simple automation?
A1: Automation performs individual tasks automatically (e.g., starting a server), while orchestration coordinates multiple automated tasks across environments, handles dependencies and scales resources.
Q2: Why is hybrid cloud becoming more popular now?
A2: Rising cloud costs, data‑residency laws, latency requirements and vendor lock‑in concerns push enterprises toward hybrid strategies that offer flexibility, performance and compliance.
Q3: How does Clarifai help with hybrid cloud orchestration?
A3: Clarifai’s compute orchestration provides a vendor‑agnostic control plane to deploy AI models on any hardware or environment. It offers autoscaling, GPU fractioning, local runners and containerized packaging, reducing costs and improving reliability.
Q4: What are some key challenges of hybrid orchestration?
A4: Challenges include complexity and skill gaps, latency management, security risks, cost control, vendor lock‑in and regulatory compliance. Mitigation requires training, automation, zero‑trust security and FinOps practices.
Q5: How will AI shape the future of orchestration?
A5: AI will enable predictive scaling, self‑healing infrastructure and agentic operations, reducing downtime and energy consumption. It will also drive FinOps 2.0, quantum integration and carbon‑aware scheduling.

Developer advocate specialized in Machine learning. Summanth work at Clarifai, where he helps developers to get the most out of their ML efforts. He usually writes about Compute orchestration, Computer vision and new trends on AI and technology.
Developer advocate specialized in Machine learning. Summanth work at Clarifai, where he helps developers to get the most out of their ML efforts. He usually writes about Compute orchestration, Computer vision and new trends on AI and technology.
© 2023 Clarifai, Inc. Terms of Service Content TakedownPrivacy Policy






© 2023 Clarifai, Inc. Terms of Service Content TakedownPrivacy Policy