
API
Enabled Secure Data Hosting (SDH) feature for all users
- SDH is now enabled for all users. This is a critical, breaking change. If you are an API user, follow the guide here.
- At Clarifai, we use the Amazon S3 storage service to host user-provided inputs. Additionally, we’ll be introducing Secure Data Hosting (SDH) as an extra layer of security and access control to the data stored on Amazon S3.
- Secure Data Hosting simply works as a proxy over the Amazon S3 storage service. It acts as an intermediary or middleman, allowing authorized users to access the content stored on Amazon S3. When a user with the necessary authorization tries to access an SDH URL, it will retrieve the corresponding content from the associated S3 URL, and display it to the user.
- The SDH service uses a token-based authorization mechanism to grant access. All inputs are fetched from the hosted service only with an authorized token—the tokens are issued after a proper user authentication as part of the Clarifai platform login process.
- By employing secure data hosting as a proxy over Amazon S3, we enhance the security of users’ data while leveraging the robust storage and infrastructure capabilities provided by Amazon S3. The SDH service helps us to ensure that users’ inputs remain protected and can only be accessed by authorized individuals or systems.
Community
Published several new, ground-breaking models
- Published General-English-Image-Caption-Blip-2, a scalable multimodal pre-training method that enables any Large Language Models (LLMs) to ingest and understand images. It unlocks the capabilities of zero-shot image-to-text generation.
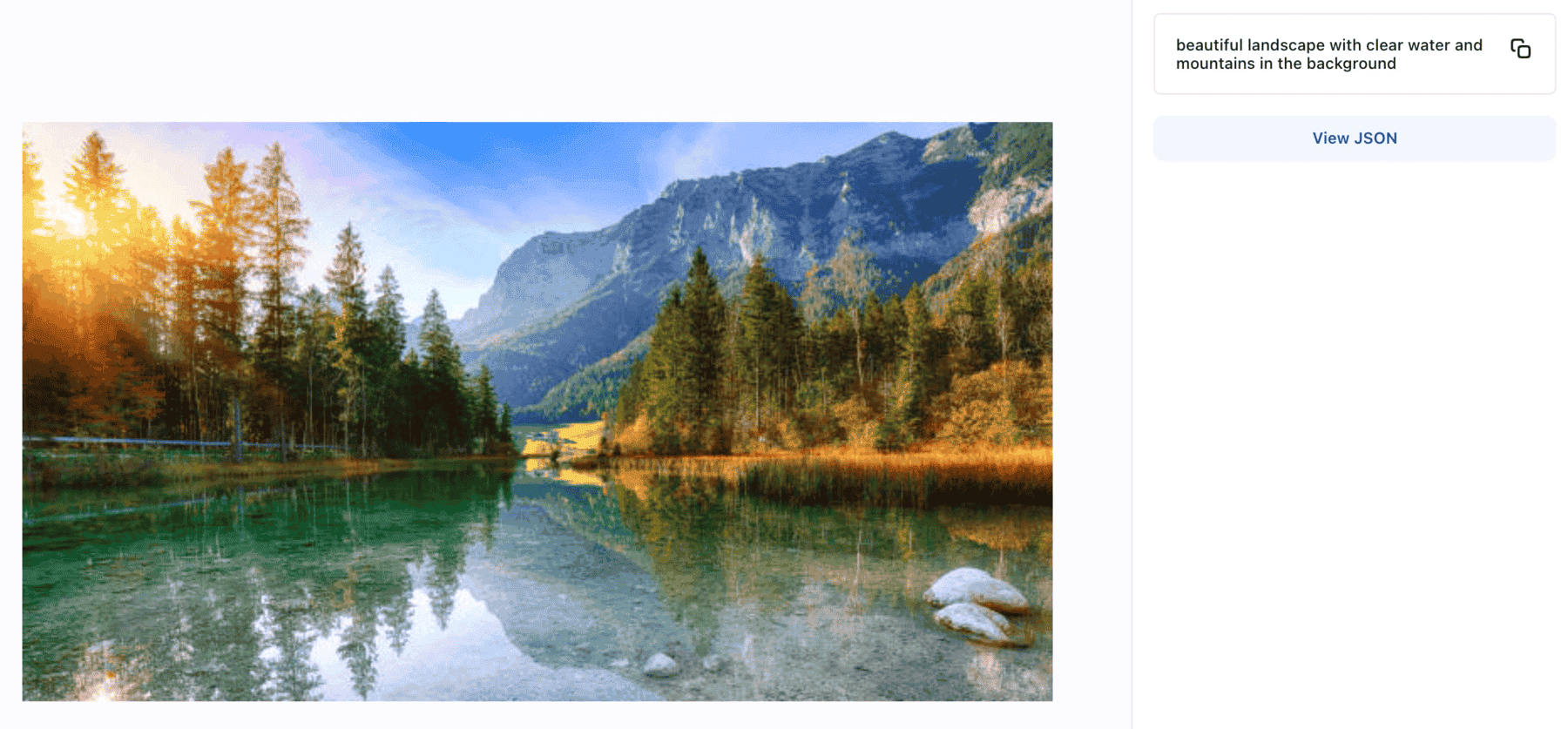

- Published Falcon-7B-Instruct, a 7B parameters LLM based on Falcon-7B and fine-tuned on instructions and conversational data; they thus lend better to popular assistant-style tasks.
- Published Hkunlp_Instructor-XL, an embedding model that can generate text embeddings tailored to any task (e.g., classification, clustering, text evaluation, etc.) and domains (e.g., science, finance, etc.) by simply providing the task instruction, without any fine-tuning.
- Published Llama2-7B-Chat, a fine-tuned LLM from Meta that is optimized for dialogue use cases.
- Published Llama2-13B-Chat, a fine-tuned LLM from Meta that is optimized for dialogue use cases.
- Published Text-Bison, a foundation model from GCP (Google Cloud Platform) that is optimized for a variety of natural language tasks such as sentiment analysis, entity extraction, content creation, document summaries, answers to questions, and labels that classify content.
- Published Code-Gecko, a foundation model from GCP that supports code completion. It generates new code based on the code that was recently typed by a user.
- Published Code-Bison, a foundation model from GCP that supports code generation. It generates code based on a natural language description. For example, it can create functions, web pages, and unit tests.
- Published Textembedding-Gecko, an embedding model from GCP that generates embeddings from the given text, which can be used for different language-related tasks.
- Published Detr-Resnet-101, a DEtection TRansformer (DETR) object detection model that is trained end-to-end on COCO 2017 dataset (118k annotated images).

- Published General-Image-Recognition-Deit-Base, a Data-Efficient Image Transformer (DeiT) image classification model that is pre-trained and fine-tuned on ImageNet-1k (1 million images, 1,000 classes).
- Published Claude-v2, a chat completion model from Anthropic, driven by an LLM, for generating contextually relevant and coherent responses.
- Published General-Image-Recognition-Deit-Base, a Data-Efficient Image Transformer (DeiT), state-of-the-art image classification model that is pre-trained and fine-tuned on ImageNet-1k (1 million images, 1,000 classes).
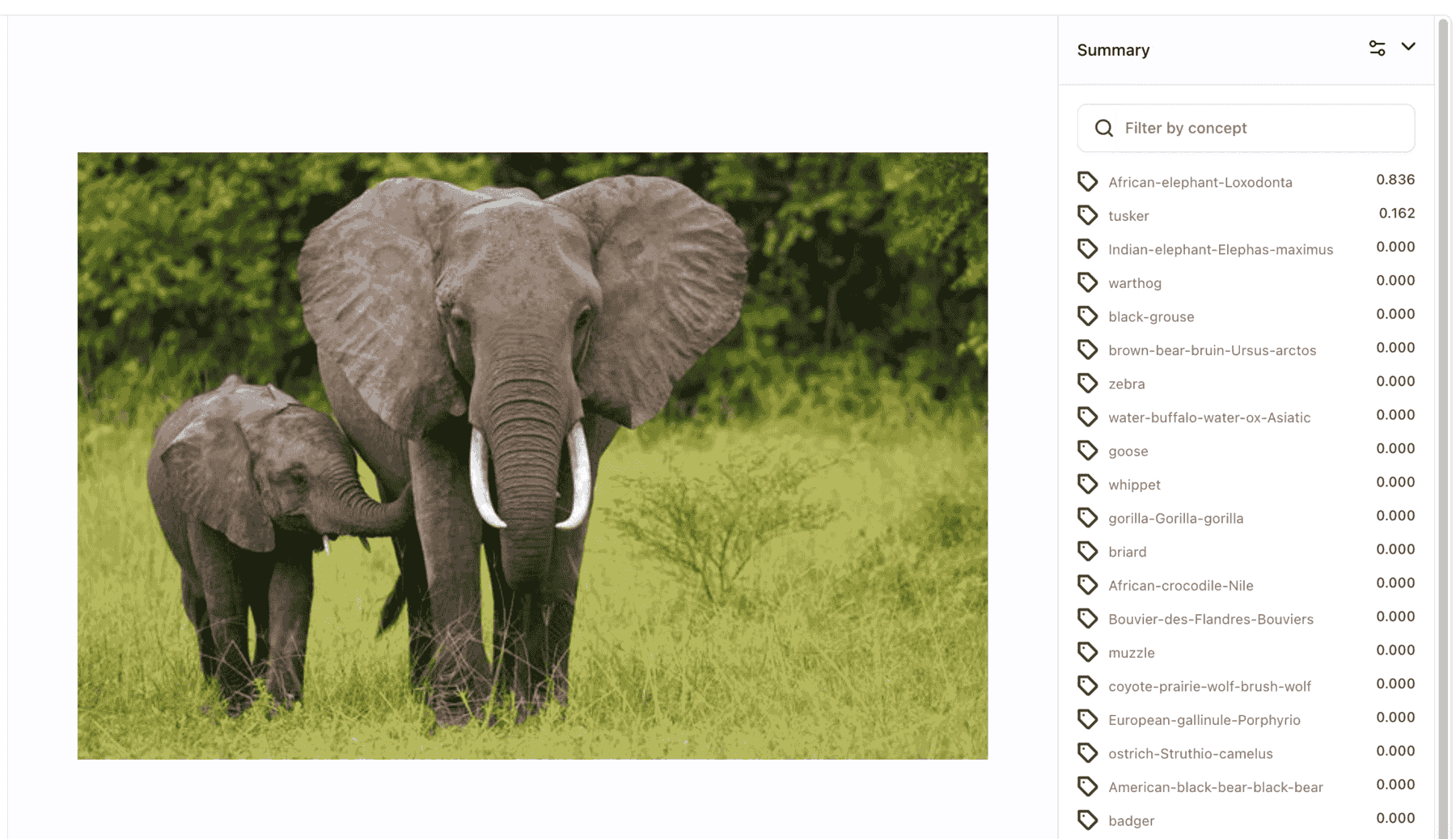
- Published General-English-Image-Caption-Blip-2-6_7B, a state-of-the-art image captioning model with 6.7B parameters.
- Published Multimodal-Embedder-Blip-2 , a scalable multimodal pre-training method that enables any LLMs to ingest and understand images. It unlocks the capabilities of zero-shot image-to-text generation.
- Published XGen-7B-8K-Instruct, a powerful 7-billion parameter LLM trained on up to 8K sequence length with fine-tuning on instructional data, enabling robust long sequence.
- Published MPT-Instruct-7B, a decoder-style transformer LLM, fine-tuned for efficient short-form instruction with 6.7B parameters.
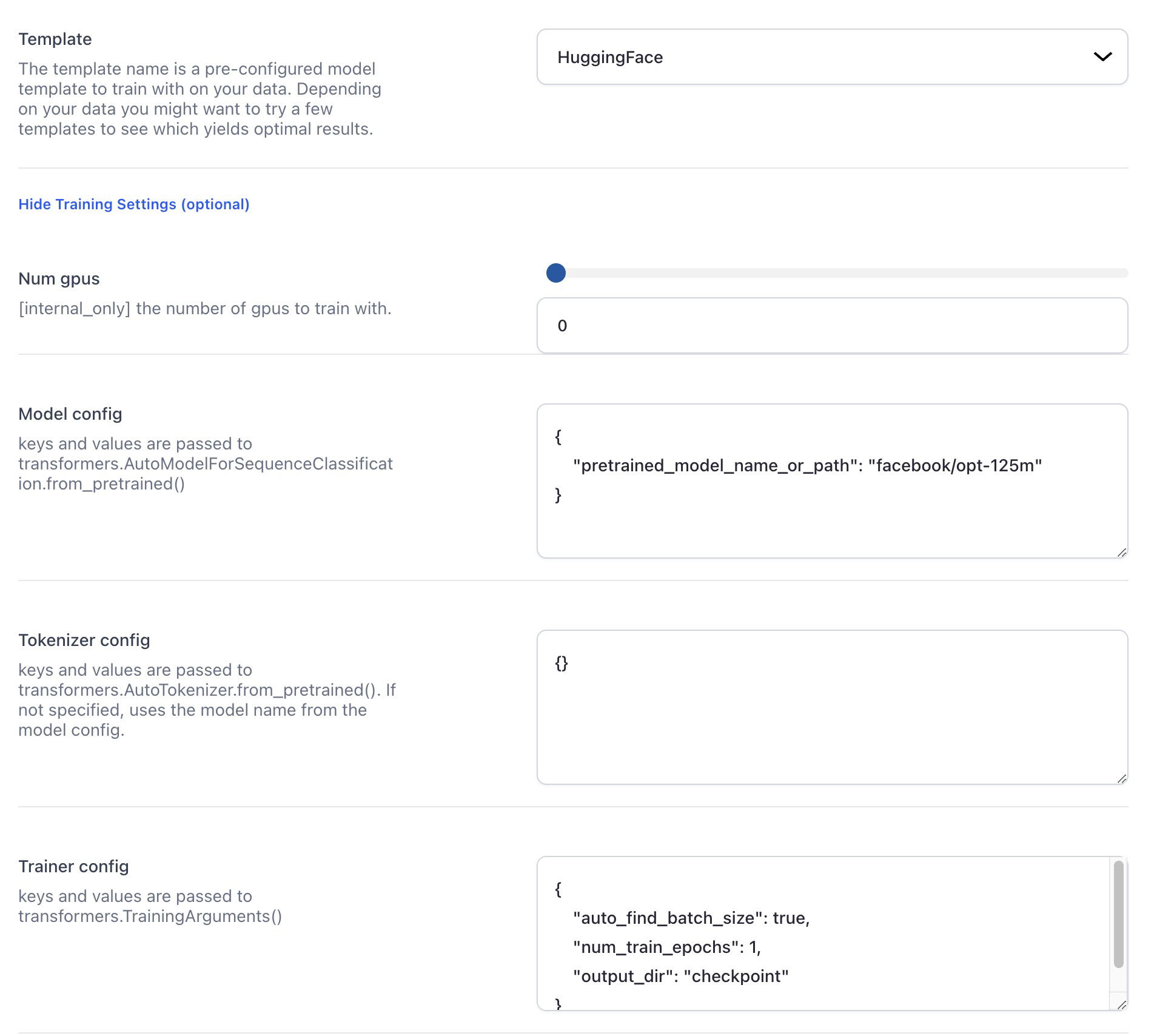
Added ability to customize Hugging Face and MMCV (OpenMMLab Computer Vision) deep training templates using the Python config file format
- You can now add your own custom model configuration when creating a text classification model using the Hugging Face deep training template.
- You can also add custom configurations to MMClassification, MMDetection, and MMSegmentation deep training templates. You can customize their loss functions, backbones, necks, heads, and more.
Bug Fixes
- Fixed an issue that caused the model evaluation process to break when numerous concepts were used. Model evaluation now works as desired.
- Fixed an issue with the A21 Jurassic generative model that caused it to cache output prompts, resulting in repetitive responses upon subsequent usage. The A21 Jurassic model now generates new responses, providing different outputs each time the page is refreshed.
- Fixed an issue where models and workflows ignored new app and user IDs. Previously, any attempts to rename an app or a user ID, or to relocate the app to an organization (equivalent to altering the user ID), resulted in the models and workflows failing to recognize these updated values. We fixed the issue.
- Fixed an issue where it was not possible to update a model's visibility. Previously, if you edited a model's visibility and published the changes, trying to edit the model's visibility again could not work. We fixed the issue.
Developer Preview with Request-Only Access
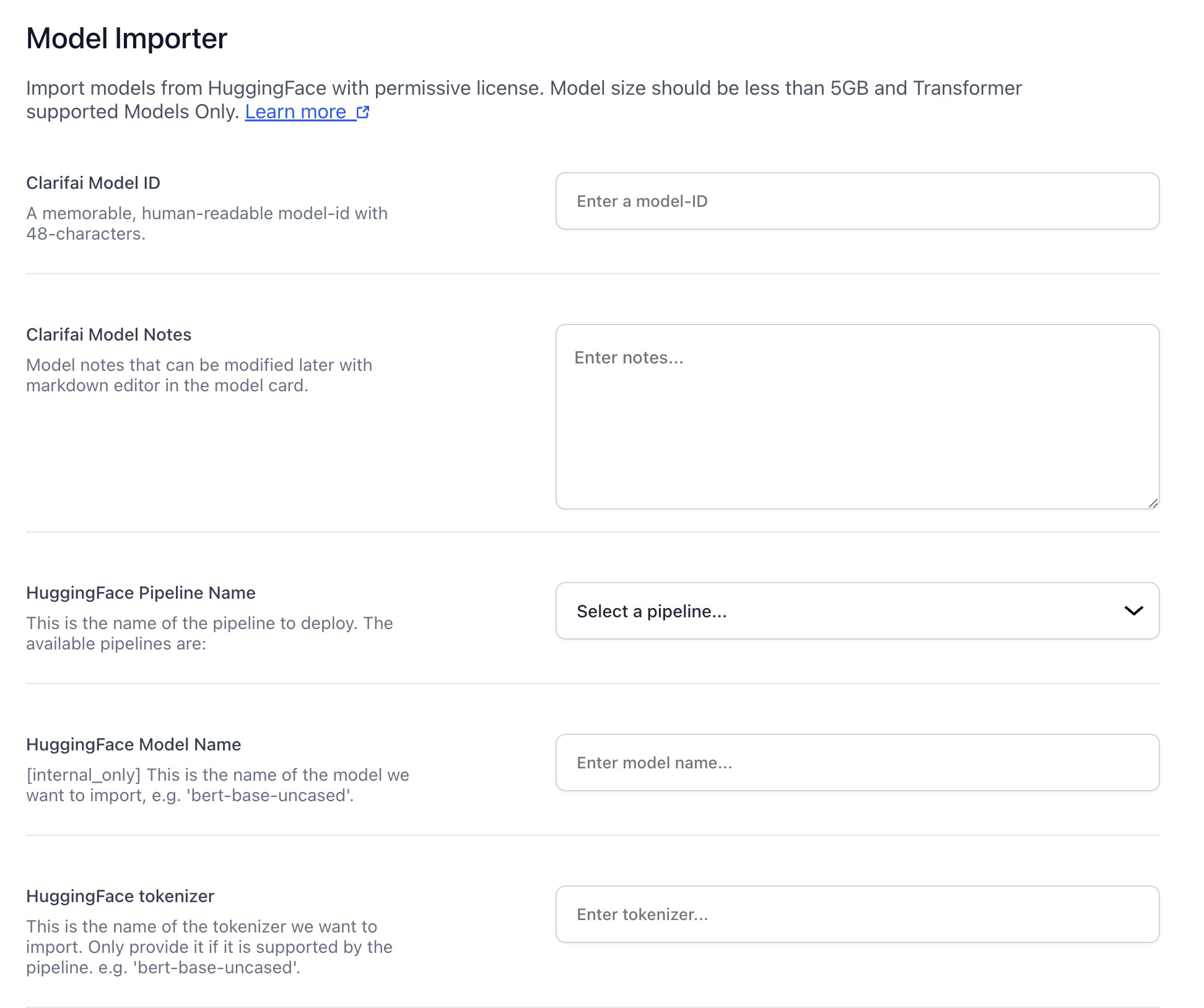
- Added ability to import models from Hugging Face. You can now import models with permissive licenses from Hugging Face and use them on the Clarifai platform.
Added ability to fine-tune text-to-text models. Advanced model builders can now further customize the behavior and output of the text-to-text models for specific text generation tasks. They can train the models on specific datasets to adapt their behavior for particular tasks or domains.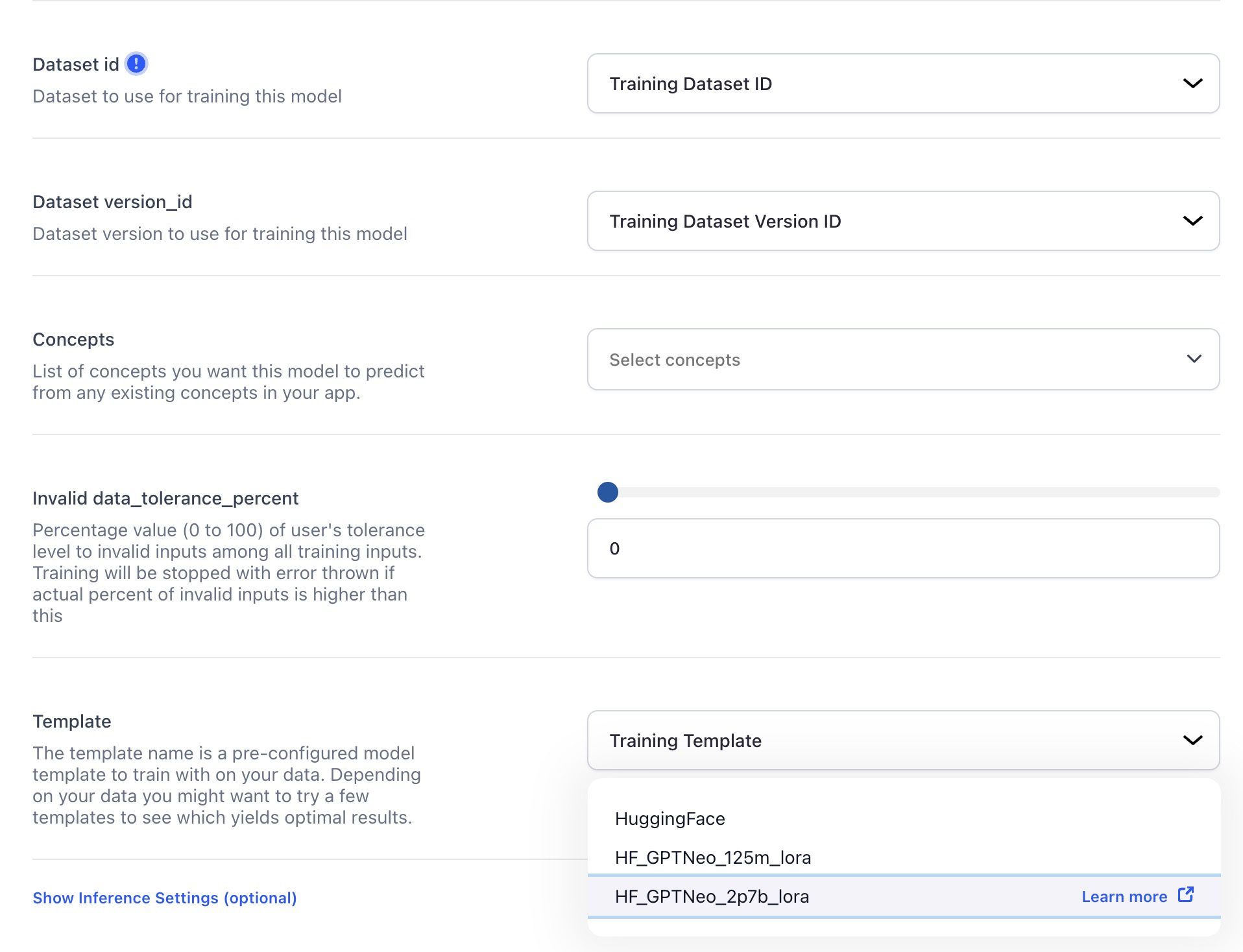
Model Page Improvements
- Reduced the width of the PAT ID field. If you click the Use Model button on a model's page, a small window will pop up. Next, if you select the Call by API tab, you'll be able to see the PAT key injected in your code samples. You can also click the Create a new token button to generate a new PAT.
- We improved the layout of the PAT ID field and the Create a new token button to enable them to fit properly in the form.
- Added app name to the model/workflow/modules tiles details. We have incorporated the app's name that corresponds to the displayed resource, offering improved clarity. Now, when you review the tile details on an individual page for a model, workflow, or module, you will notice the app's name specified in the following format: User ID / App ID.
- Created optimized UX (User Experience) for the prompter models on the Model-Viewer. We refined the way users interact with and receive output from the prompter models, aiming to make the process more intuitive, efficient, and user-friendly.
- Fixed an issue where the model page for any detection model crashed when swapping between the Overview and Concepts tabs, then back again—but only if the predicted bounding boxes were rendered previously. Previously, if you navigated to any detection model's page, waited for the model to render bounding box predictions on the Overview tab (default), and then switched to the Concepts tab, switching back to the Overview tab generated an error. We fixed the issue.
- Fixed an issue where the Create new Model page displayed a series of broken thumbnails. The thumbnails on the page are now displayed properly.
Sorting
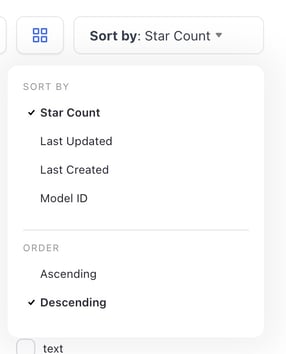
Added ability to sort by stars and adjusted "created/updated" behavior
This sorting change affects both individual and Community pages as well as all resources—apps, models, workflows, modules, and datasets.
- In addition to sorting by Name and Last Updated, we added two more options: Star Count (default option, henceforth) and Date Created.
- If a user selects Date Created, Last Updated, or Star Count, the sorting results will be displayed in Descending order (by default)—the newest, more popular items will appear first.
- If a user selects Model Name, the sorting results will be displayed in Ascending order (by default)—items will be displayed alphabetically.
Apps
Exposed apps as a new resource in the Community listing
- Just like models and workflows, you can now share, sort, and search apps in the Community.
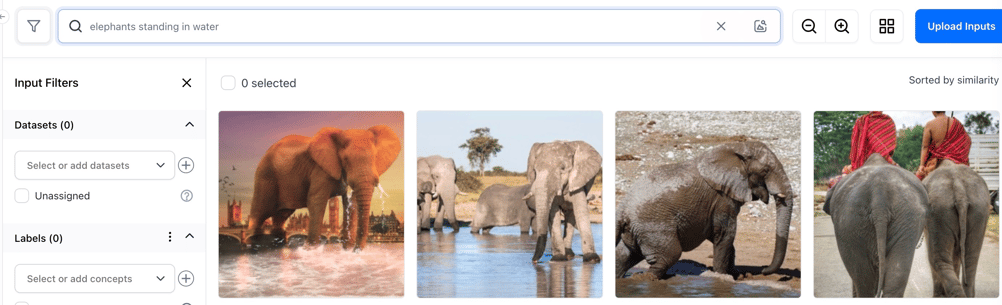
- Introduced the Smart Image Search by Caption feature on the Input-Manager. You can rank, sort, and retrieve images based on a predicted match to a query caption text. You just need to provide a caption text that best describes the images you want to search for, and the most relevant matches associated with that query will be displayed.
- Fixed an issue that caused infinite polling for inputs after uploading has been completed. You can now upload inputs successfully without experiencing any issues.
- Added ability to view estimated search result counts on the Input-Manager.
- You can now view an estimated number of inputs associated with your search results.
- Fixed an issue where uploading a CSV file of text data into a newly created dataset did not work.
You can now create a new dataset and upload CSV files with text data without encountering any issues.
- Fixed an issue that prevented the unification of Input-Manager and Input-Viewer stores. The Input-Manager and the Input-Viewer now have the same unified stores. They now display the same search results, and the list of inputs used in the inputs manager grid is the same as those used in the inputs gallery on the Input-Viewer page.
Added ability to create annotations with AI assistance on the Input-Viewer
- You can now request annotation suggestions from any model or workflow available to you on a particular input. You can then convert the suggestion into an annotation.
- Added ability to use hotkeys to switch between annotation tools on the Input-Viewer. We significantly improved the accessibility and usability of the Input-Viewer by adding a new feature that enables the use of hotkeys on the annotation tools.
Bug Fixes
- Previously, when you were using an org account, selecting “Explore on your own” on the onboarding modal created the default first app under your logged-in user's account, and not on your org user's account.
- The onboarding modal now creates the default first app under the org user's account.
- The user is also now able to see their full name displayed on the onboarding modal.
- Fixed an issue where a created PAT did not appear in the list of PATs. Previously, when you created a new PAT on the “Use in API” screen during the onboarding process, the PAT was not automatically populated and could not be used straight away, as compared to the standard "Use in API" flow on a model's page. We fixed the issue.
User Account Settings
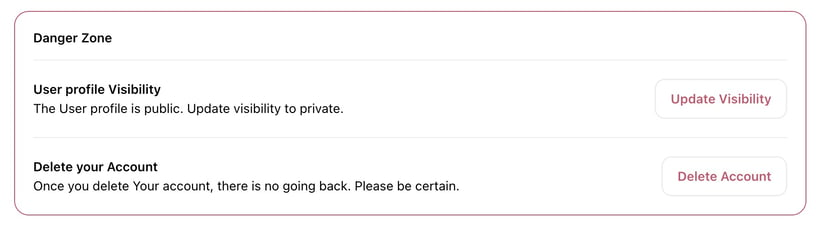
- Added ability to make a user's profile public or private.
- You can now update the visibility of your user profile to either public or private.
- You will not be able to keep any resources public if you set your user profile visibility to private.
- Added new roles on the Job Role drop-down list.
- On the Account Settings page, you will find a form that enables you to update your contact information. We have made updates to the roles listed in the Job Role field within the form.
- The new roles are also reflected in the sign-up form.
Organization Settings and Management
- Added “AppAddCollaborators” featured flag for org admins and org members. Org admins and org members now have the “AppAddCollaborators” featured flag, which enables them to add collaborators to an app.
- Fixed an issue where an org contributor was not allowed to authorize or uninstall Installed Module Versions (IMV). An org contributor role now has sufficient scopes to successfully authorize or uninstall IMVs.
- Fixed an issue where a team member was not allowed to view or use IMVs. A team contributor or member role now has sufficient scopes to successfully view or use IMVs.
Modules
- Improved the handling of GitHub repository URLs with trailing slashes. We enhanced the way we handle the importation of modules from Streamlit app repositories on GitHub with trailing slashes ("/") at the end of their URLs.
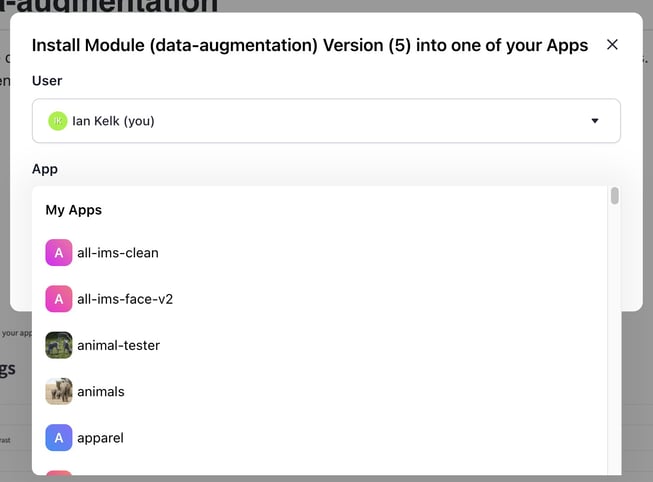
- Improved the design of the Install Module pop-up modal. If you click the Install Module button at the upper-right corner of an individual module page, a small modal will pop up.
- We've improved the design of the modal to allow you to select a destination organization where you want to install the module. Previously, you could solely select a user.
- Increased the deployment time for the module manager. Previously, when you created a new module, the deployment timed out after 5 minutes. If the module required a longer time to build, the module deployment failed after 5 minutes. We increased the deployment time for the module manager from 5 minutes to 10 minutes.
- Updated the module manager to set secrets that modules can use. You can now set environment variables and secrets for module versions as you create them.
- Allowed anonymous usage of the LLM Battleground module. You can now anonymously use the module to compare the performance of large language models. You do not need to log in to the Clarifai platform before using it.
- Added a warning to be displayed before deleting a module version. We added a warning informing a user that deleting a module version will uninstall each of its install instances.
- Added a directory to prevent modules from breaking libraries. Previously, we encountered a bug that was hindering modules from writing temporary files, leading to the disruption of certain Python packages during runtime. We fixed the issue.
- Fixed a bug that prevented getting commits from GitHub repository branches. We fixed a Module-Manager bug that caused errors when getting commits from GitHub repository branches.
Secure Data Hosting (SDH)
Previously, when SDH was enabled on the Portal, cross-user app copying did not work. Previously, when SDH was active, duplicating an app you are added as a collaborator resulted in the destination app having broken inputs. On the other hand, duplicating your own apps worked just fine. We fixed the issue.
Labeler
- Fixed an issue that prevented annotations from being created while working on a task. You can now successfully add annotations when labeling tasks.
Workflows
- Fixed an issue where selecting concepts from the workflow visual graph builder resulted in an error. Previously, selecting concepts for a model node in the workflow visual graph builder resulted in an empty list. We fixed the issue.






















